How effective is your automation test suite?
How impactful is it for your product and your team?
Do you know how to grow your test suite without sacrificing quality and performance?
These questions are surprisingly difficult to answer — especially when your entire suite feels like it’s constantly on fire, your tests are untrustworthy, and production bugs are popping up like they’re going out of style. (Just me?)
To bring some clarity — and because testers love pyramids — I created the Automation Maturity Pyramid as a way to measure automation impact.
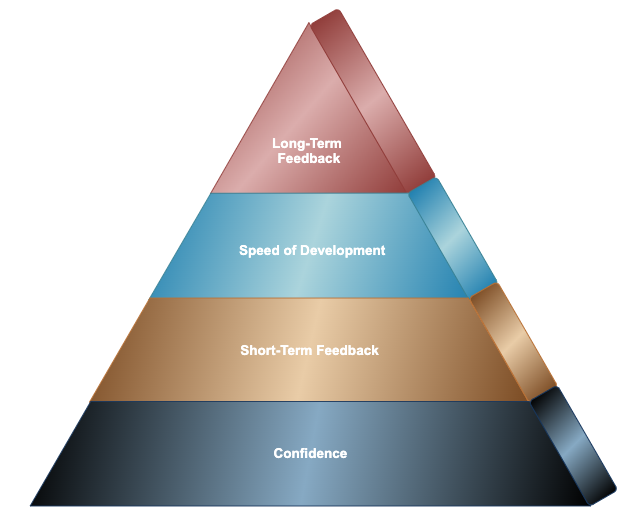
First, let’s remember why we write automation tests in the first place. At the end-of-the-day, automation tests should support two simple missions:
- Increase product quality & confidence
- Accelerate development & deployment
So when we think about the pyramid and its phases, everything we do should ultimately align with those missions.
The pyramid has four levels of maturity:
- Confidence — Trusting your test results.
- Short-Term Impact — Creating value in daily development.
- Speed of Development — Scaling automation without slowing down.
- Long-Term Impact — Sustaining trust, visibility, and continuous improvement.
Each phase builds on the one below it. Later stages only unlock their benefits once the initial foundation is solid. The pyramid is both tool and type agnostic, meaning you can apply it to any automation suite, framework, or testing type that fits your needs.
Remember, this journey takes time. Think of the pyramid as a compass, not a checklist to rush through. If you’re starting fresh, it’ll guide you from the beginning. If you already have a suite, it’s a framework to measure current impact and decide what to tackle next.
Phase 1 — Confidence
A pyramid collapses without a strong base. The same is true with automation. If teams don’t trust the test failures (or even successes), everything else becomes meaningless.
When results are unreliable, people stop acting on them. And when tests are ignored, automation loses its purpose. In many ways, unreliable automation is often worse than not having any at all.
The Tests Must Pass
Failures will happen. That’s not the issue. The danger is when teams normalize broken tests or flaky failures. Every red test should be taken seriously: investigated, understood, and resolved. While there are exceptions, the default culture must be: stop and fix. Adopt the mindset “all tests must pass”, and technical debt will quickly diminish before it starts. A mature automation test suite starts with an accountable mindset.
What Undermines Confidence
- Flakiness: Tests that pass or fail inconsistently without code changes. Common causes include race-condition, non-deterministic app behavior, dependent tests or poor test data management.
- Environment Instability: Where you will run your tests matter, especially if multiple options are needed. Can you guarantee tests will run reliably across all environments?
- Weak Data Strategies: Do tests always have the data they need? Is it static or dynamic? A strong data strategy reduces countless downstream failures. My favorite data management is through programmatic control.
Phase 1 is about establishing trust. Once failures are credible and environments stable, your suite stops being noise and starts being a safety net. A small, confident test suite is more impactful than a large, unstable one. Some actions items to consider:
- Research and implement flake-reduction practices for your tool of choice
- Create a culture of accountability: quarantine flaky tests and resolve them quickly
- Write tests environment-agnostically
- Define a consistent test data strategy that works across environments
If you’ve done these, you’re ready for Phase 2.
Phase 2 — Short-Term Impact
With trust established, the next step is to make automation useful right now. Tests should provide fast feedback and reduce risk during daily development.
If tests only run occasionally or if results arrive too late to act on, they don’t influence decision-making. The goal is to make automation an indispensable partner for developers, not a background chore.
This phase is all about defining an initial CI/CD strategy that suites your team’s development processes.
CI/CD Strategy
A good rule: the closer tests run to code changes, the more valuable they are. Running suites pre-merge ensures failures tie directly to specific commits, not multiple layers of changes. Fewer variables mean quicker triage.
Nightly or scheduled runs still have a place — especially for full regressions, but the longer the gap between code and results, the harder it is to debug.
Some common strategies:
- Pre-merge Tests: Run in under ~10 minutes. Cover critical paths first, then expand with performance in mind.
- Full Nightly Regression: Capture broader coverage where speed isn’t urgent.
- Custom Tag-Based Gates: Sub-groups of tests run based on criteria.
Results Visibility
Running tests is meaningless if no one notices the outcomes. Ensure results are clear, fast, and shared.
Every suite should generate artifacts accessible to all engineers. This includes screenshots, video, error logs and any other additional test information. Without proper artifacts, debugging failures becomes exponentially harder. Additionally, notifications should be immediate and integrated into tools your teams already use.
A professional rule of mine— act like Veruca Salt from Willy Wonka:
“I want those results and I want them now!”

Remember, Phase 2 is about usefulness. Once tests deliver fast, actionable feedback, they directly help teams ship better code, quicker. Developers know within minutes when a real-bug is introduced. Testers know when flake is first introduced, for immediate remediation.
Stick to the mantra: “all tests must pass”.
Once you start getting short-term feedback from your tests, it’s time to optimize them.
Phase 3 — Speed of Development
Once automation is trusted and embedded in the workflow, the focus shifts to efficiency. The question becomes: how can automation help us move faster without cutting corners?
At small scale, almost any automation adds value. But as suites grow, inefficiency turns automation into a bottleneck. Tests that take hours to run or are painful to debug become blockers instead of enablers. This phase has three areas of focus: writing, debugging and executing tests.
Write Tests Faster
Writing tests faster primarily comes down to test organization and structure. Expanding further:
- Standardize Structure: Use any pattern that makes sense to you and don’t worry about perfection. Any organization beats spaghetti-code chaos. Optimize over-time.
- Reuse Aggressively: Create helpers, builders, and shared libraries for scaleability.
- Proactive Test Planning: Review product tickets early to avoid last-minute gaps.
- Use AI-assisted Tooling: Just do it. There’s no excuse not to use AI anymore. Embrace our new overlords!
- Document: Look, we all know it sucks…but providing guides and common gotchas reduce ramp-up time as the team grows. What would past you wish they had when they first onboarded?
Debug Tests Faster
Test failures will happen so response time makes or breaks a suite’s value.
- Prioritize Readability: Choose clarity over cleverness; smaller, focused tests are easier to diagnose. Always write tests with future you in mind. “Will this make sense to me in six months?”.
- Reduce Variables: Run tests as close to the change as possible (prioritize pre-merge if not already implemented).
- Culture of Accountability: Build a habit of immediate triage: treat all fails with the same urgency so at least some resolution occurs.
- Improved Artifact Tools: Interactive runners, browser devtools, and in-depth logs are gold. Improve artifacts as needed.
Run Tests Faster
This one is simple. How fast do our tests run? Repeat after me: “Nobody brags about a three-hour test suite”. As the test suite grows, will the team still get quick value without slowing down the process?
- Parallelize: Split suites across multiple machines or containers. A must for pre-merge pipelines.
- Subset Tests: Run critical paths first; save broader regressions for later. Customize based on need and overall test performance.
- Optimize Code: Remove hard-coded waits, reduce unnecessary DOM interactions, apply tool best practices.
Phase 3 is about efficiency. Automation should accelerate delivery, not drag it down. When done well, it enables rapid iteration and frequent, confident releases. All of a sudden our monthly releases can now be reduced to weekly. Then daily. Then maybe even multiple times a day, if you’re feeling extra daring. All thanks to your automation test suite.
You deserve a raise.
Phase 4 — Long-Term Impact
The final phase is about sustainability. Once automation is fast, useful, and trusted, it must also deliver long-term value.
Teams and products evolve. Without continuous investment, automation rots: tests get flaky, results get ignored, and the pyramid crumbles. Which is all super sad. Professional advice, don’t be sad.
Long-term impact ensures automation remains a source of truth while showcasing just how cool your team is.
Metrics Inform, Not Punish
This phase is purely about responding to metrics, but use them wisely. Metrics should guide investment, not assign blame. Focus on impactful metrics that guide your automation roadmap. Simply, you don’t know what to improve if you don’t know what’s ineffective.
Some Suggestions:
- Test Coverage: Directional, not definitive. Pair with quality checks.
- Pass/fail and flake rates: Indicators of credibility.
- Execution time: Is the suite scaling with the team?
- Time-to-resolution (TTR): How quickly do teams fix failures?
- Defect detection efficiency (DDE): Percentage of bugs caught by automation.
If possible, consider augmenting these with a dashboard where visibility is further increased. Visual trends make it easier to consume historical trends and identify weaknesses. Plus bar graphs are fun and line graphs always look convincing. Don’t even threaten me with a good time and bring up pie charts.
This phase is small but important. It’s the culmination of all the previous phases, and purely intended to bring visibility into how well things went in the previous phases. It drives future revisions and ensures the test suite is never stagnant in it’s impact.
Phase 4 is all about trust at scale. Mature automation creates transparency, informs investment, and continues to improve over time.
Putting It All Together
The Automation Maturity Pyramid is a lot smaller than the Pyramids of Giza but much more relatable since those are real and in Egypt and this is thought-leadership and about testing. Just to clarify any confusion to this point.
But seriously, it’s about measuring your impact, one phase at a time. Building a successful automation test suite is hard without proper guidance. There’s many technical steps and failures can quickly become overwhelming and frustrating.
To recap:
- Confidence First: You have to trust your tests, always. The rest will follow.
- Early Wins: No matter the test suite size, obtain value. Start catching real issues.
- Take small steps: Steady improvements compound into big gains. Efficiency is a learning curve and only obtained through experience.
- Welcome Failures: Hello failures, come on it. Have a seat. Let’s talk about how you’re making my current life bad so we can make my future life good.
- Celebrate Progress: Building a reliable, impactful suite is a team achievement. Be proud of that green test run, those first 100 tests, or the first real-bug your suite caught. You’re a rockstar, genuinely.
Done well, automation isn’t overhead — it’s a strategic advantage. Build a base of trust, create fast feedback loops, optimize for speed, and commit to long-term transparency. That’s how you turn test automation into a driver of product success.
Best of luck in your climb. And as always, happy testing.











