Testing gRPC APIs
Major platforms like Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Kubernetes, and Envoy leverage gRPC’s capabilities in their high-performance services.
Without further ado, let’s start with some pre-requisites:
- Install Git https://git-scm.com/downloads
- Install VS Code: https://code.visualstudio.com/download
- Install Node JS from https://nodejs.org/en
- Install PlayWright Extension in VS Code: https://playwright.dev/docs/getting-started-vscode
Setting up local gRPC Server
After making sure all pre-requisites have been followed, first let’s start by having our local gRPC product service available. Follow the steps given below to have the service available:
- Open the page “https://github.com/nsharmapunjab/frameworks_and_tools/tree/main/grpc_tools/gRPC_sample_server” and follow the instructions given on the page to clone the repo.
- Open the cloned repo in VS Code
- Run “npm install” command in terminal to install the dependencies
- Then run “node server.js” command, with this it will start the server at “http://127.0.0.1:50051/”
On a high-level, this gRPC service is a simple server for managing products. It provides three main functionalities: adding a product, retrieving a product by its ID, and listing all products. Below is an explanation of each functionality with examples:
Add Product
The addProduct function allows clients to add a new product to the server.
Example Request:
{
"name": "Laptop",
"description": "A high-end gaming laptop",
"price": 1500.00
}Example Response:
{
"product_id": 1,
"message": "Product added successfully"
}Get Product
The getProduct function allows clients to retrieve a product by its ID.
Example Request:
{
"product_id": 1
}Example Response:
{
"product_id": 1,
"name": "Laptop",
"description": "A high-end gaming laptop",
"price": 1500.00
}3. List Products
The listProducts function allows clients to retrieve a list of all products.
Example Request:
{}Example Response:
{
"products":
[
{
"product_id": 1,
"name": "Laptop",
"description": "A high-end gaming laptop",
"price": 1500.00
}
]
}Excellent work! Our gRPC APIs under test are operational.
Now let’s perform some steps to see if this is working on not, try to play with it in Postman by following the guide here: https://learning.postman.com/docs/sending-requests/grpc/first-grpc-request/
You should be able to see three methods as shown below:
Develop Automated Tests
Now everything is up and running, so let’s start automating gRPC API testing with our favorite tool i.e. Playwright. Follow steps given below to have some automated tests to validate the APIs:
- To create a base Playwright project using the VS Code extension: Open VS Code and create a new folder named “grpc-tests”.
- Open the terminal and follow the instructions provided at https://playwright.dev/docs/intro.
- The above step will generate the basic project structure with sample tests in the “tests” folder.
- Run “npx playwright test” in the terminal to execute the tests. The results will be displayed in the terminal. Nice work, now you have Playwright project setup to start with.
- Delete all the tests files under tests and tests-examples folders.
- Open the terminal in VS Code and run following command to install the required dependencies:
npm install @playwright/test @types/node @grpc/grpc-js @grpc/proto-loader protobufjsPurpose of Libraries
=====================
@playwright/test: A testing framework for end-to-end testing with Playwright.
@types/node: TypeScript type definitions for Node.js.
@grpc/grpc-js: The gRPC library for Node.js, used to create and manage gRPC
clients and servers.
@grpc/proto-loader: A library to load .proto files for use with grpc-js.
protobufjs: A library for working with Protocol Buffers in JavaScript.7. Create a folder “proto” under main folder i.e. grpc-tests folder, create a product.proto file under this folder and add following content (This is the API schema file Protobuf file for the service under test):
syntax = "proto3";
package product;
service ProductService {
rpc AddProduct (AddProductRequest) returns (AddProductResponse) {}
rpc GetProduct (GetProductRequest) returns (GetProductResponse) {}
rpc ListProducts (ListProductsRequest) returns (ListProductsResponse) {}
}
message AddProductRequest {
string name = 1;
string description = 2;
double price = 3;
}
message AddProductResponse {
int32 product_id = 1;
string message = 2;
}
message GetProductRequest {
int32 product_id = 1;
}
message GetProductResponse {
int32 product_id = 1;
string name = 2;
string description = 3;
double price = 4;
}
message ListProductsRequest {}
message ListProductsResponse {
repeated Product products = 1;
}
message Product {
int32 product_id = 1;
string name = 2;
string description = 3;
double price = 4;
}The product.proto file defines the structure and services for a gRPC API that
manages products. This file is used to generate the necessary code for the
client and server to communicate using gRPC.
Syntax and Package
===================
syntax = "proto3";: Specifies that this file uses Protocol Buffers "version 3".
package product;: Defines the package name as product.
Service Definition
====================
service ProductService: Defines a gRPC service named ProductService with three
methods:
AddProduct: Adds a new product.
GetProduct: Retrieves a product by its ID.
ListProducts: Lists all products.
Message Definitions
====================
AddProductRequest: The request message for adding a product, containing name,
description, and price.
AddProductResponse: The response message for adding a product, containing
product_id and message.
GetProductRequest: The request message for retrieving a product, containing
product_id.
GetProductResponse: The response message for retrieving a product, containing
product_id, name, description, and price.
ListProductsRequest: An empty request message for listing products.
ListProductsResponse: The response message for listing products, containing a
list of Product messages.
Product: A message representing a product, containing product_id, name,
description, and price.8. Create a folder “utils” under main folder i.e. grpc-tests and create a grpcClient.ts file under this folder and add following content
import * as grpc from '@grpc/grpc-js';
import * as protoLoader from '@grpc/proto-loader';
import * as path from 'path';
// Load the protobuf
const PROTO_PATH = path.resolve(__dirname, '../proto/product.proto');
const packageDefinition = protoLoader.loadSync(PROTO_PATH, {
keepCase: true,
longs: String,
enums: String,
defaults: true,
oneofs: true,
});
const productProto = (grpc.loadPackageDefinition(packageDefinition) as any).product;
// Create a gRPC client
const client = new productProto.ProductService('localhost:50051', grpc.credentials.createInsecure());
export { client };
export const listProducts = async () => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
client.listProducts({}, (error: any, response: any) => {
if (error) {
reject(error);
} else {
resolve(response);
}
});
});
};
export const addProduct = async (request: any) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
client.addProduct(request, (error: any, response: any) => {
if (error) {
reject(error);
} else {
resolve(response);
}
});
});
};
export const getProduct = async (request: any) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
client.getProduct(request, (error: any, response: any) => {
if (error) {
reject(error);
} else {
resolve(response);
}
});
});
};This file sets up a gRPC client to interact with a gRPC server using a
protobuf definition.
Imports:
grpc: The gRPC library for Node.js.
protoLoader: A library to load .proto files.
path: A Node.js module for handling file paths.
Load the Protobuf:
==================
The path to the .proto file is resolved using path.resolve.
protoLoader.loadSync loads the protobuf definition from the specified file.
The loaded definition is then used to create a gRPC service client.
Create a gRPC Client:
=====================
A gRPC client is created for the ProductService defined in the protobuf,
connecting to a server running on localhost:50051.
Export the Client and API Functions:
The client is exported for use in other parts of the application.
listProducts: An asynchronous function that calls the listProducts method on
the gRPC client and returns a promise.9. Now create a test file under the “tests” folder with name “product.spec.ts”, and add following contents:
import { test, expect } from '@playwright/test';
import { client, listProducts, addProduct, getProduct } from '../utils/gprcClient'
var productId = 0;
test.beforeAll('Get the max product id', async () => {
console.log('Fetching the list of products...');
const response = await listProducts() as { products: { id: number }[] };
const products = await response.products;
if (products.length > 0) {
productId = Math.max(...products.map((product: any) => product.product_id));
}
console.log(`Max product ID found: ${productId}`);
});
test('Add Product API to add product', async () => {
const request = { name: "Macbook 14 inches M4", description: "Latest M4 Macbook Pro", price: 4000.0 };
console.log('Adding a new product:', request);
const response = await addProduct(request);
console.log('Add Product Response:', response);
expect(response).toEqual({ message: 'Product added successfully', product_id: productId + 1 });
});
test('Get Latest Product Details', async () => {
const request = { product_id: productId + 1 };
console.log('Fetching details for product ID:', request.product_id);
const response = await getProduct(request);
console.log('Get Product Response:', response);
expect(response).toEqual({ name: 'Macbook 14 inches M4', description: 'Latest M4 Macbook Pro', price: 4000.0, product_id: productId + 1 });
});
test('Add Product API to check validation', async () => {
const request = { name: "Macbook 14 inches M4", description: "", price: 4000.0 };
console.log('Adding a new product with invalid data:', request);
const response = await addProduct(request).catch(error => ({ message: error.message, code: error.code }));
console.log('Validation Error Response:', response);
expect(response).toEqual({ message: '3 INVALID_ARGUMENT: Name, description, and price are required', code: 3 });
});The main purpose of the tests in the product.spec.ts file is to verify the
functionality of the product-related APIs in a gRPC service. Specifically,
the tests aim to -
Fetch the maximum product ID: Before running the tests, the beforeAll hook fetches
the list of products and determines the maximum product ID. This is used to
ensure that new products are added with a unique ID.
Add a new product: The first test (Add Product API to add product) checks if a
new product can be successfully added to the system. It verifies that the
response contains a success message and the correct product ID.
Get details of the latest product: The second test (Get Latest Product Details)
retrieves the details of the newly added product and verifies that the response
contains the correct product information.
Validate product addition with invalid data: The third test (Add Product API
to check validation) attempts to add a product with invalid data (missing
description) and checks if the appropriate validation error is returned.10. Run the tests by running “npx playwright test” command in terminal :
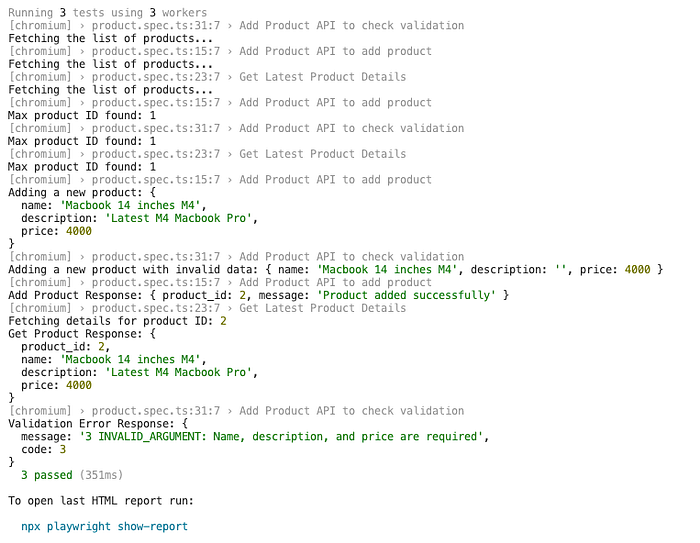
Excellent work on automating your first gRPC API!
Should you encounter any problems, please feel free to leave a comment here or contact me via LinkedIn.
Ready to dive deeper? Try writing a test that verifies the API returns a “Product not found” error when you use a product_id that doesn’t exist.
In conclusion,
Grasping the fundamental purpose of the new API architecture (gRPC) was key to our ability to create effective testing methods and automation for these APIs. I hope this article can assist learning and approach to testing with this new API architecture. Looking forward to your feedback or suggestions.
Keep learning! In the next article, we’ll explore a different API architecture and its testing strategy.
